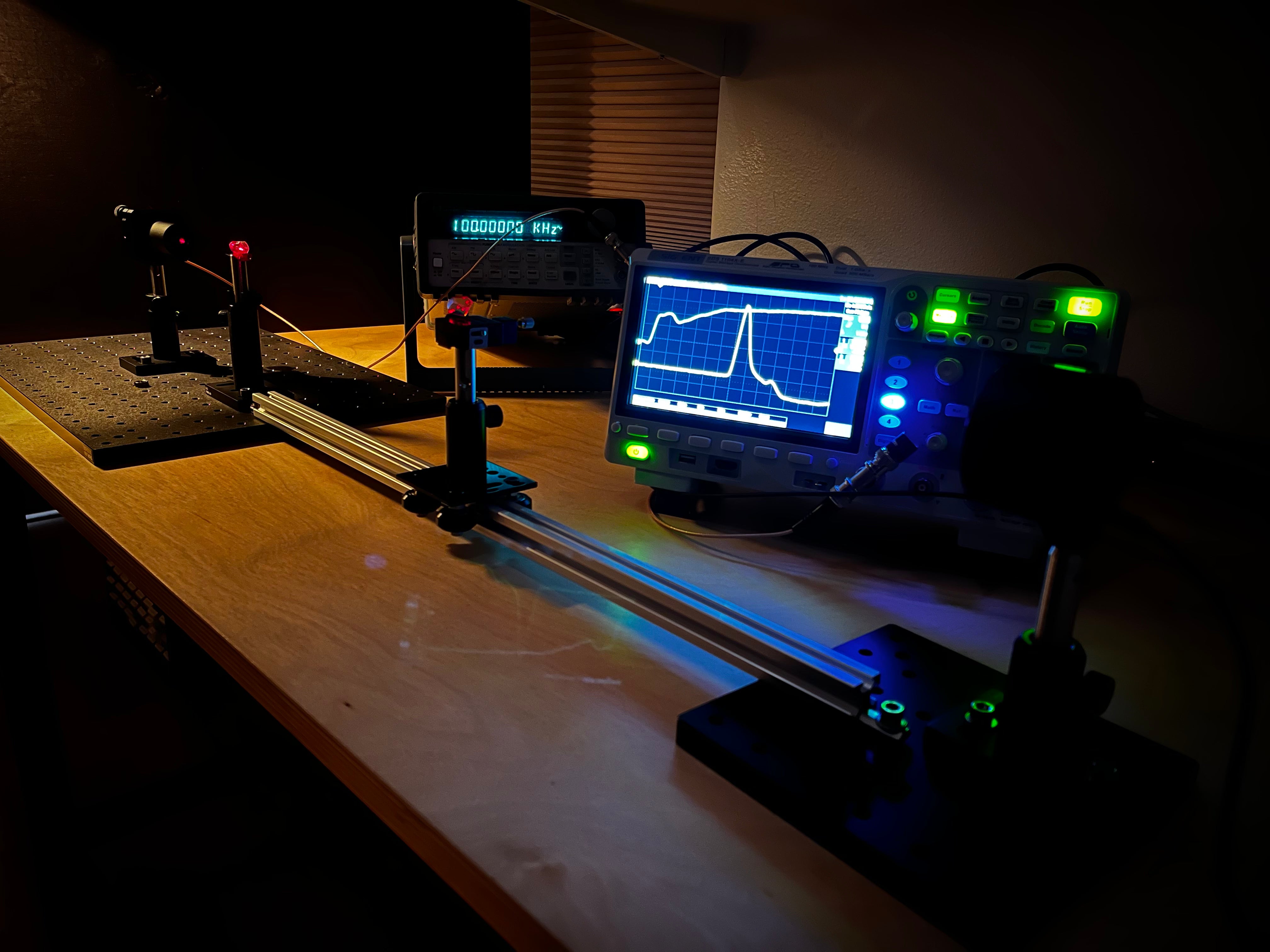
Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Diode
Regular price
$340.00
Sale price
$340.00
Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Diode
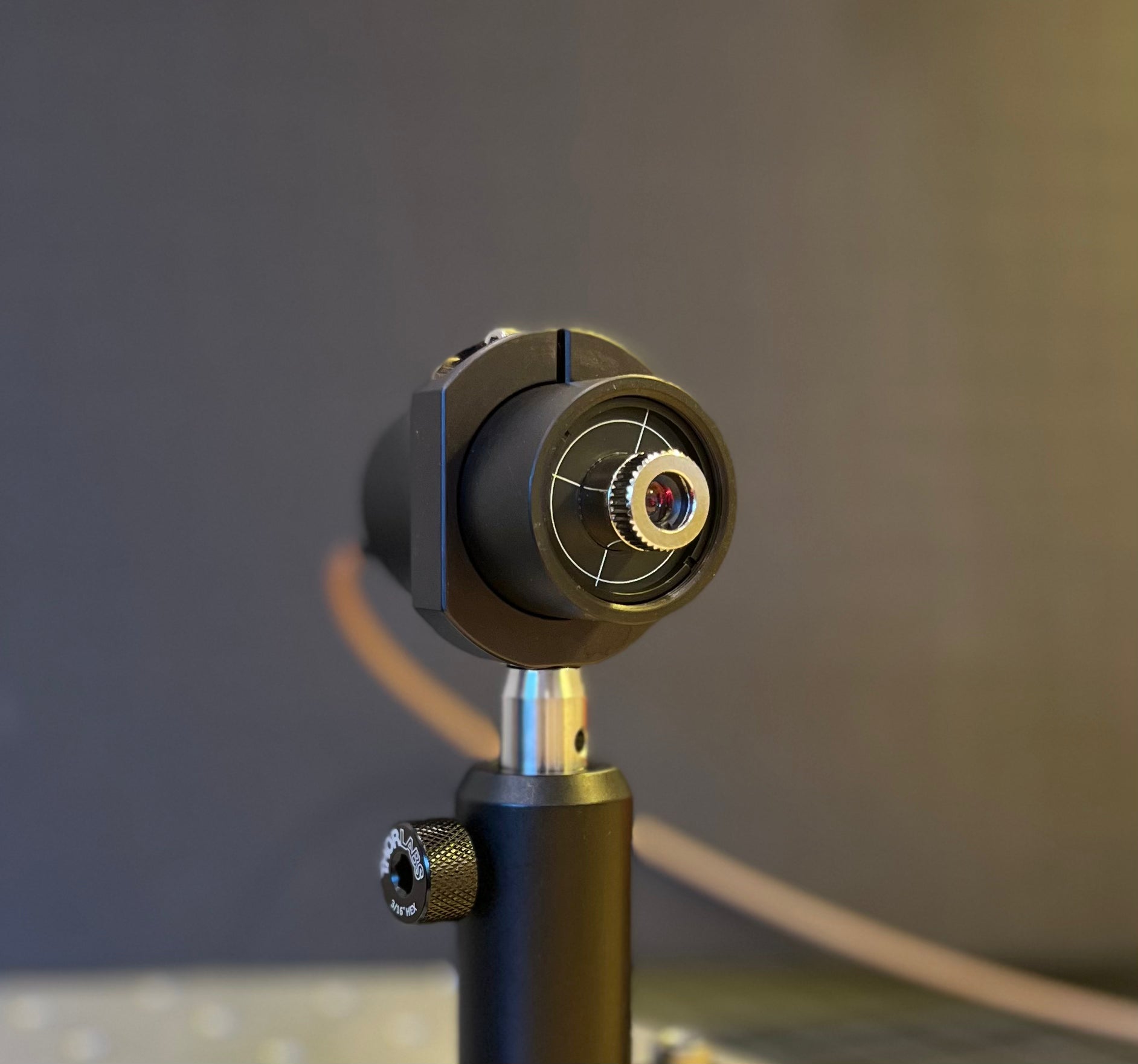



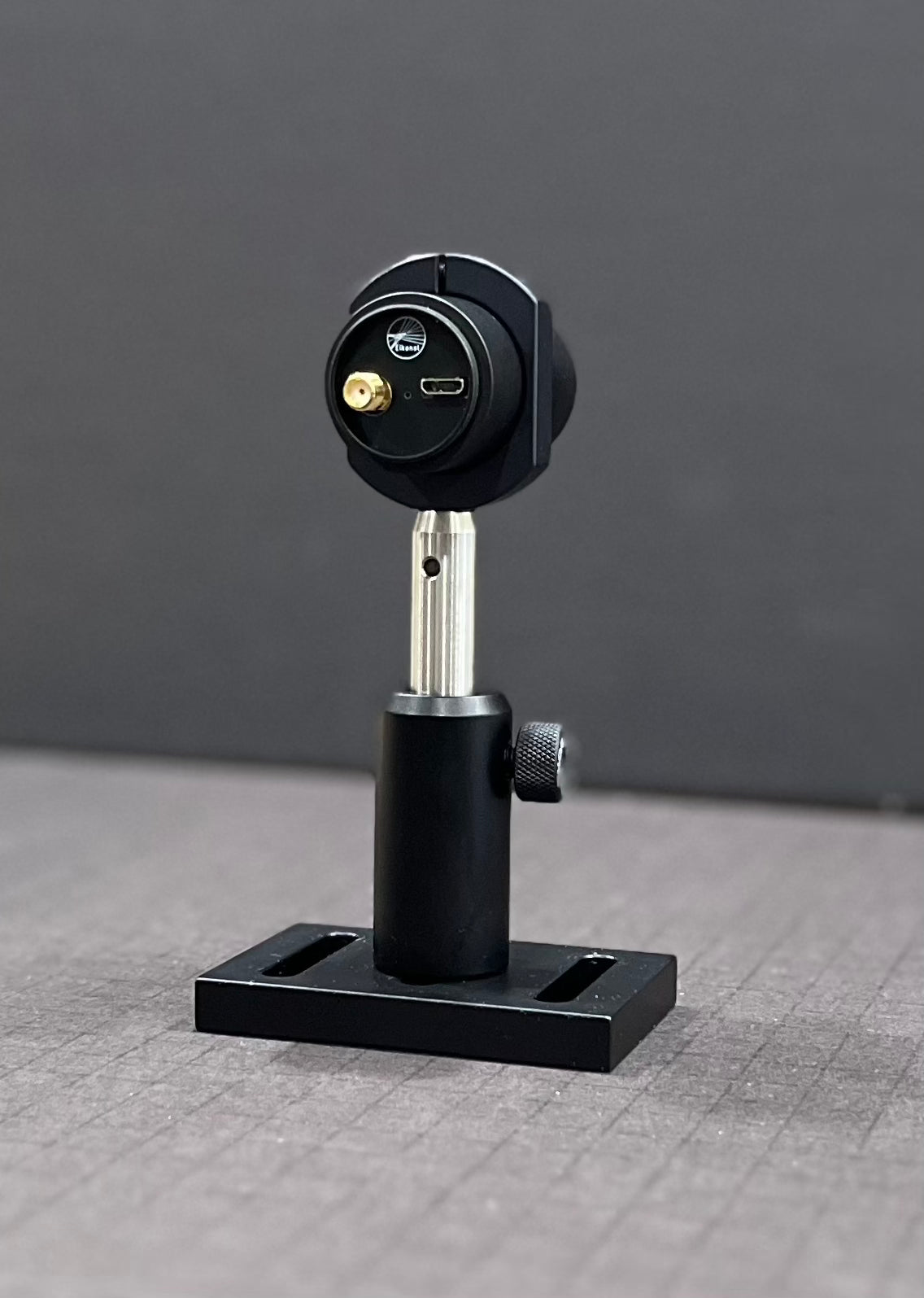
Specifications


Product added to cart






